Start of topic | Skip to actions
2D Euler equations - Explosion in a Box
Variation of GuC-Factor (situation at time t=0.5)
Results: 2 Levels / 3 Levels / Variation of Distribution / Variation of GuC-Factor
The Grid-Unit-Coarsening-Factor defines the minimal size of a unit of the base grid that is used for partitioning. For instance, a GuC-Factor =4 means, that units of 4x4 base cells are used. Higher GuC-Factors simplify partitioning, but usually lead to load-imbalance. If a relatively fine base grid is used, larger GuC-Factors can speed up the partitioner drastically (see example Backward facing step). The default value is 2.
Workload for different GuC-factors - Distribution with Hilbert space filling curve. 4 computing nodes are used.
| GuC-Factor | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 |
| 2 | 0.932 | 1.062 | 1.044 | 0.962 |
| 4 | 0.914 | 1.097 | 1.057 | 0.931 |
| 8 | 0.778 | 1.433 | 0.843 | 0.946 |
GuC-Factor=2
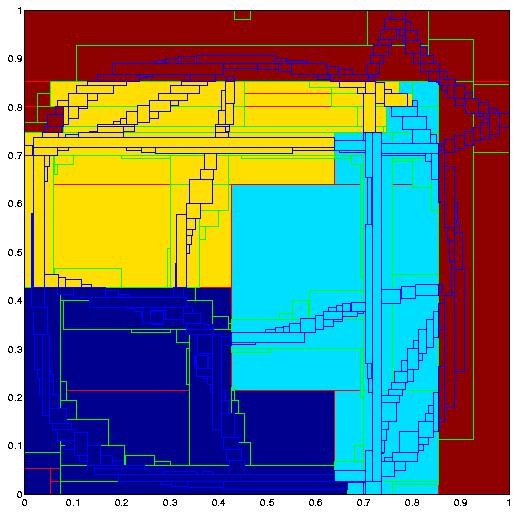
GuC-Factor=4

GuC-Factor=8

Benchmark
| Task | GuC-Factor=2 | GuC-Factor=4 | GuC-Factor=8 | |||
| s | % | s | % | s | % | |
| Integration | 2246 | 67.2 | 2182 | 65.8 | 2163 | 60.2 |
| Flux correction | 180 | 5.4 | 201 | 6.1 | 275 | 7.6 |
| Boundary setting | 315 | 9.4 | 386 | 11.6 | 636 | 17.7 |
| Recomposition | 496 | 14.9 | 453 | 13.7 | 426 | 11.8 |
| Clustering | 37 | 1.1 | 34 | 1.0 | 32 | 0.9 |
| Misc. | 56 | 2.0 | 52 | 1.9 | 52 | 1.7 |
| Total / Parallel Efficiency | 3329 | 85.1 | 3307 | 85.7 | 3733 | 75.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<--- Problem description
-- RalfDeiterding - 04 Dec 2004