Start of topic | Skip to actions
Impulse generation by an open shock tube
Problem Description
We performed numerical studies of a shock tube with an open end to investigate the impulse due to the exhaust of gases through the open end of the tube as a model for a partially-filled detonation tube as used in pulse detonation engine testing. The simulaion model is shown in the following. The driver section was filled with pressurized gas (helium or nitrogen) and the driven section was open to the atmosphere. The initial conditions in the driven section matched those of the room, nominally 22 C and Pa = 99 kPa. In the driver section, the initial temperature was also room temperature, but the initial pressure was varied from P0 = 929 kPa (P0/Pa = 9.38) to P0 = 198 KPa (P0/Pa = 2.0). The length of the driver section, L0 = 101.6 mm, the total tube legth L = 0-1.84 m, the tube diameter d0 = 39.5 mm. The fill fraction,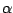 , is defined as
, is defined as 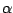 =L0/L. The effects of the pressure ratio and the fill fraction were examined.
=L0/L. The effects of the pressure ratio and the fill fraction were examined.
Numerical Simulation
- Two dimensional (planar), inviscid, non-reactive Euler equations with the perfect gas equation of state.
- Two constant polytropic exponents,
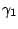 and
and 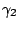 representing gases in both driver and driven sections.
representing gases in both driver and driven sections.
- Explicit second order Godunov-type numerical scheme incorporating a hybrid Roe-solver-based method.
- AMR-computation with coarse resolution of 0.9875 mm; two additional refinement levels, with a refinement factor 2 and 4 respectively.
Results
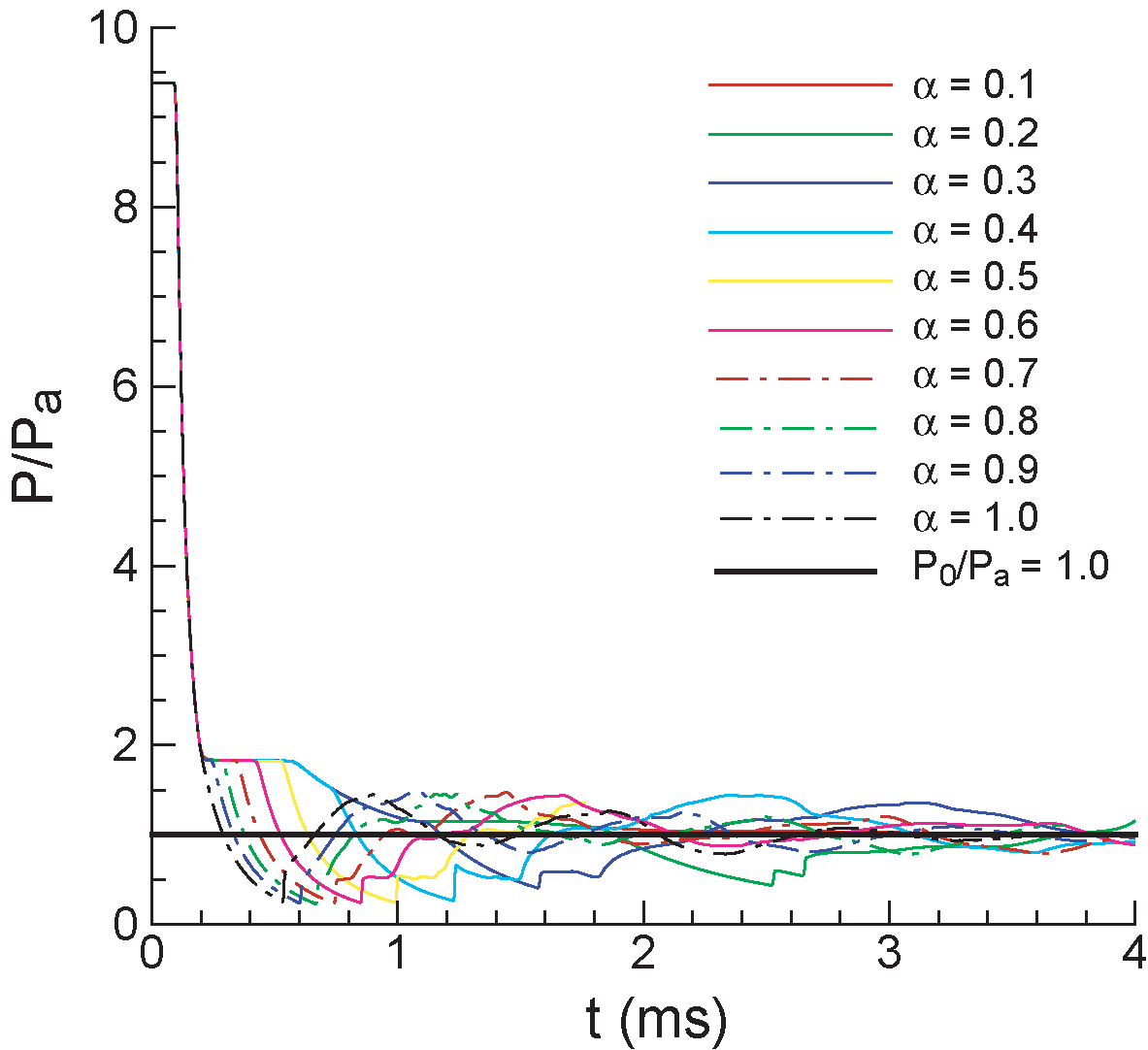
- Average pressure on the thrust wall
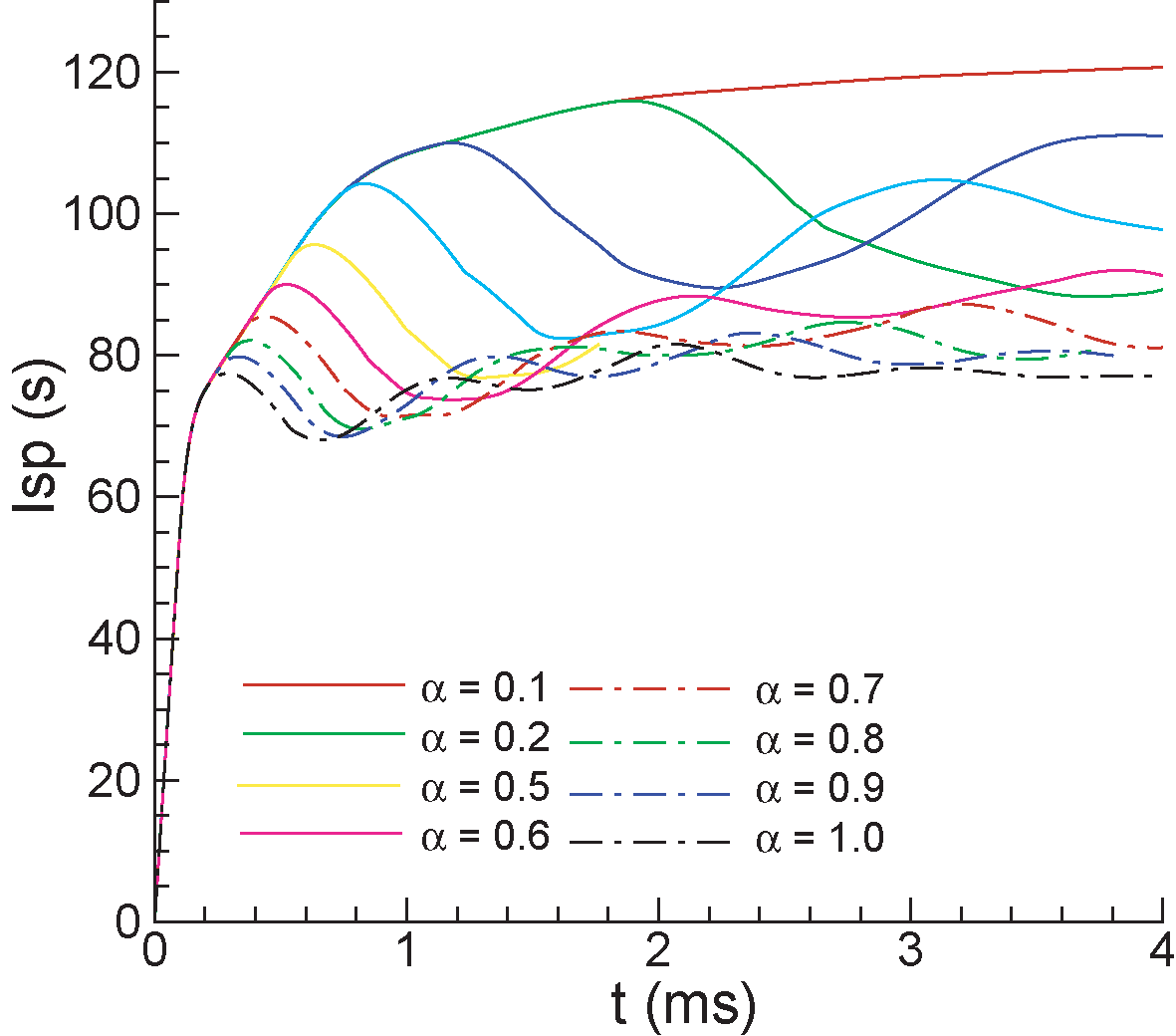
- Impusle on the thrust wall
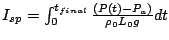
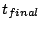 is the final time reached in the simulation,
is the final time reached in the simulation, 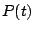 is the average pressure on the thrust wall,
is the average pressure on the thrust wall, 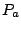 is the ambient pressure,
is the ambient pressure, 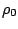 and
and 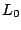 are the gas density and the tube length of the driver section respectively.
are the gas density and the tube length of the driver section respectively.
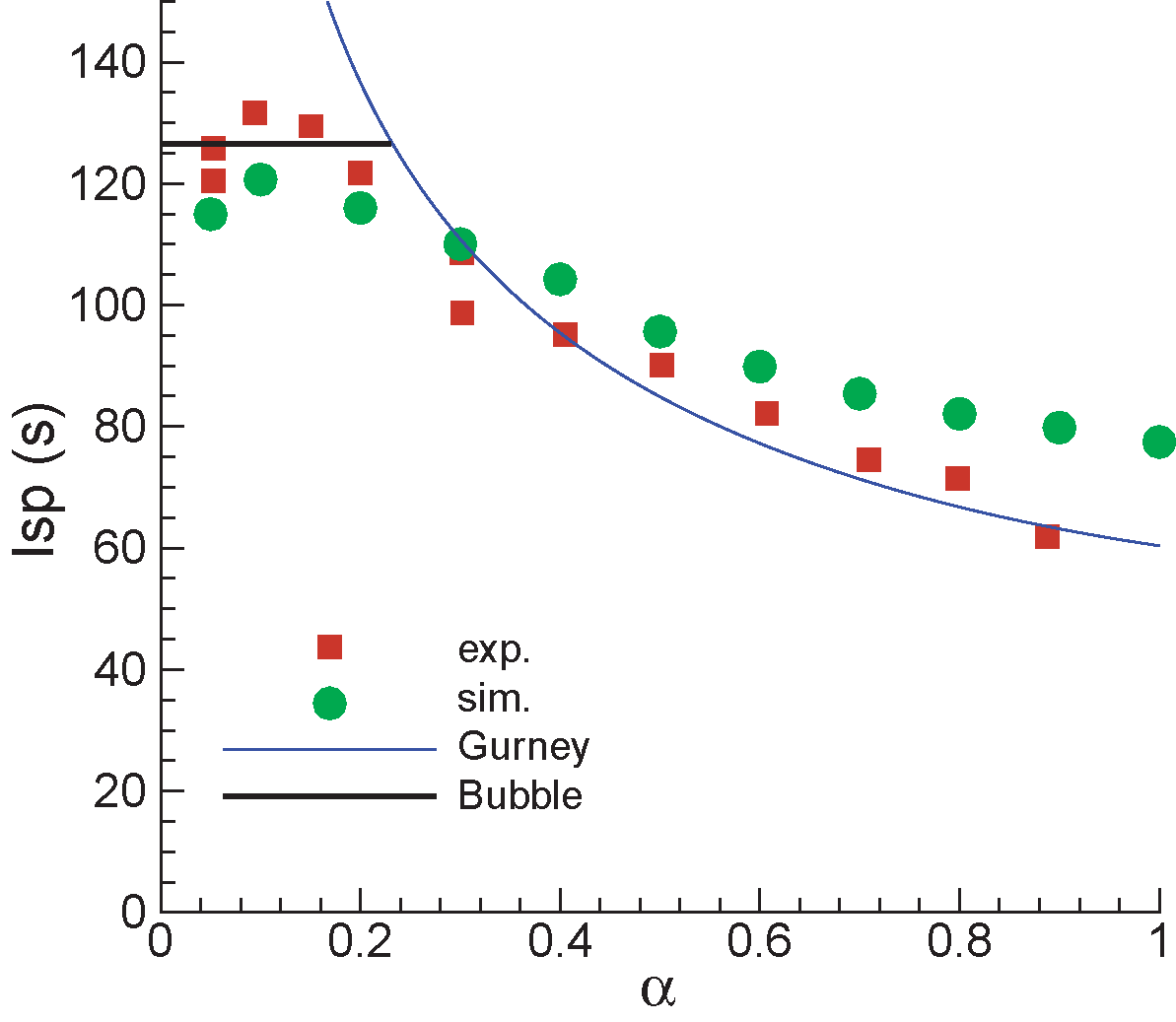
- Comparison of specific impulse given by experiments, simulations and theories.
- Reference: J. Kasahara, Z.~Liang, S.T. Browne and J.E. Shepherd, 2006, Impulse Generation by an Open Shock Tube, subimitted to J. AIAA. PDF version of this paper
| I | Attachment  | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | model_shock.gif | 12.6 K | 22 Aug 2006 - 15:40 | ZheLiang | Simulation Model |
| | Pre_t_ff_He_P9.gif | 18.3 K | 22 Aug 2006 - 20:59 | ZheLiang | average pressure on the thrust wall |
| | Isp_t_ff_He_P9.gif | 18.5 K | 22 Aug 2006 - 21:00 | ZheLiang | Impulse |
| | P_ff1.0_He.mpg | 133.4 K | 22 Aug 2006 - 21:31 | ZheLiang | Pressure field |
| | compare_He_P9.gif | 13.3 K | 25 Aug 2006 - 23:08 | ZheLiang | comparison |
| | shocktube.pdf | 854.5 K | 25 Aug 2006 - 23:22 | ZheLiang | Paper |