2D Euler equations - Ramp
Problem description
This well-know example has been inspired by studies of planar shock-waves being reflected from wedges. A self-similar flow with a triple-point between incident shock and reflecting wall occurs. This example uses time-dependent physical boundary conditions at the upper boundary.Initial / Boundary Conditions
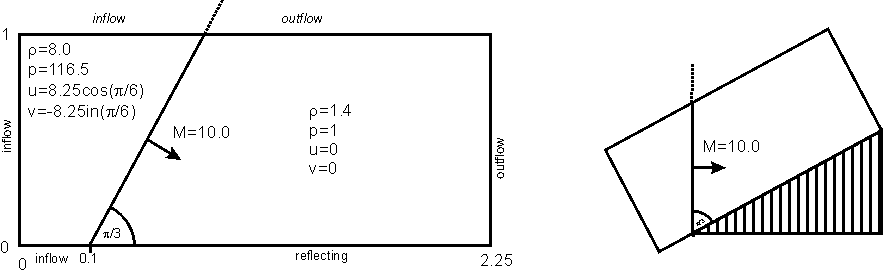
Numerical Simulation
- Two-dimensional Euler-equations for an ideal gas (Air with gamma=1.4)
- Wave propagation scheme with Minmod wave-limiter and transverse wave propagation
- Calculation with CFL-No. 0.8 to time t=0.09
- AMR-computation with a coarse grid of 250x110 cells
- Calculation of 247 time steps
- 1 levels with refinement factor 2 is used.
- Finest level corresponds to 500x220 grid (0.11 M cells)
- Calculation of 263 time steps
- 2 levels with refinement factor 2 and 4 are used.
- Finest level corresponds to 2000x880 grid (1.76 M cells)
Results: 2 Levels / 3 Levels
-- RalfDeiterding - 05 Dec 2004