2D Euler equations - Forward facing step
Problem description
A stationary mach 3 flow hits a rectangular step. A stable shock-wave pattern with a characteristic mach-stem top of the corner develops after a few time units. This well-known test problem problem demonstrates AMROC's capabilities for multiblock domains. No special entropy correction is applied to cells at the corner. Instead, a numerical method with higher numerical dissipation is chosen to obtain a stable solution.Initial / Boundary Conditions
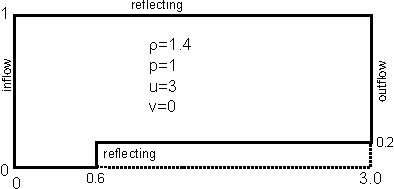
Numerical Simulation
- Two-dimensional Euler-equations for an ideal gas (Air with gamma=1.4)
- Dimensional splitting, Van Leer solver, MUSCL variable reconstruction with Van Albada limiter
- Calculation with CFL-No. 0.95 to time t=4.0
- AMR-computation with a coarse grid of 120x40 cells
- Calculation of 703 time steps
- 1 levels with refinement factor 2 is used .
- Finest level corresponds to 240x80 grid (19 K cells)
- Calculation of 317 time steps
- 2 levels with refinement factor 2 and 4 are used .
- Finest level corresponds to 960x320 grid (307 K cells)
Results: 2 Levels / 3 Levels
-- RalfDeiterding - 04 Dec 2004